What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Advantages and Development Prospects
Just a few years ago, the complete centralization of the financial system was unquestionable. This meant that government agencies, municipal and corporate institutions had full control over the process of money issuance and distribution. A classic example would be a traditional bank where clients deposit their money and also have access to loans and credit. Moreover, banks are typically overseen by a Central Bank, which guarantees reliable execution of transactions and transfers for all parties.
The drawback of such a system is excessive bureaucratization. For instance, many clients find the loan application process to be a real ordeal, but even collecting all the numerous documents doesn't guarantee a positive outcome. The presence of additional intermediaries also negatively impacts the cost of the final product.

The active development of blockchain technology, particularly smart contracts, allows us to solve this problem. Now any two people can establish reliable value exchange without intermediaries, which significantly saves time for all process participants and reduces overall costs. The collection of solutions for financial decentralization has been given the general name DeFi.
Below, we propose to examine in more detail what DeFi represents. You'll also learn how to practically use decentralized finance – particularly decentralized applications, wallets, exchanges, and so on.
What is Decentralized Finance? Ecosystem and Key Categories
Decentralized finance allows various financial operations to be performed, such as trading, lending, and others, without the participation of intermediaries in the form of financial organizations and regulatory bodies. The practical tool in this case consists of decentralized applications based on smart contracts. They can be deployed on various blockchain platforms, whose characteristics will determine the number of available offerings, commission sizes, etc. One of the most popular is Ethereum. More detailed information about it is provided below.
DeFi Ecosystem
The concept of a DeFi ecosystem is distinguished separately, which includes a set of services and technologies for fast and reliable financial operations. For example, DeFi infrastructure has its own databases, analogues of credit and deposit agreements, and transaction processing systems. Naturally, such a system cannot function without its own money, which consists of both classic cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, as well as dollar and euro-backed tokens – stablecoins.
It's important to note that the structure of financial processes here can be quite complex, as there's the possibility of combining operations, which centralized financial institutions don't allow. For instance, you can invest a certain amount of coins for interest and use it as collateral to obtain a loan. It's also worth noting that the DeFi ecosystem is currently growing at a very rapid pace, increasing its total value locked several times each year.
Areas of DeFi Use
DeFi technologies are currently most actively used in the following areas:
1. Decentralized exchanges – this is currently one of the most popular applications of blockchain in finance. Many users are already familiar with how centralized cryptocurrency or other exchanges work. However, decentralized exchanges have a fundamental difference. It lies in the fact that operations are conducted peer-to-peer (P2P), directly between users without unnecessary intermediaries. Here, each person stores coins in their own wallet and only conducts specific transactions through the exchange. Transaction security is ensured by smart contracts.
2. Decentralized derivatives Although such decentralized contracts don't yet have widespread popularity, they shouldn't be overlooked. Many traders choose this trading method because they want to reduce risks when making deals. This is achieved by fixing prices. They differ from classic derivatives in that they represent "synthetic assets" that imitate underlying assets. This means trading can involve, for example, synthetic stocks of major companies. As a result, price tracking occurs using blockchain technologies, eliminating the need for intermediaries (brokers).
3. Deposits. For DeFi applications, having a liquidity pool is important. It's from these funds that loans, credits, insurance, etc., are subsequently issued. Such pools are created through user deposits. Unlike classic deposits, they have the following features: non-fixed interest rates, as they directly depend on activity; no deposit limits; the ability to withdraw the entire amount at any time – users are provided with special tokens that they can exchange back for their coins at any time.
4. Lending. Thanks to DeFi, loans and credits become more accessible. While banks require clients to open accounts, make deposits, or prove their financial status to obtain even small amounts, decentralized finance eliminates all these barriers. The main criterion is only having digital assets that can be used as collateral for obtaining credit.
5. Stablecoins. Such coins are pegged to certain stable assets (for example, the dollar or oil prices), making their volatility lower than other cryptocurrencies. Initially, stablecoins existed within centralized platforms. However, they've recently become available in decentralized systems. The peculiarity of these coins is that they're issued through over-collateralization, and anyone can verify the issuer's reserves and ensure currency stability.
6. Payments. Despite cryptocurrency use itself opening new possibilities for paying for goods or services, DeFi has gone even further. Decentralized finance allows organizing payment processes on a "streaming" principle, where amounts are paid in portions, for example, as products are used.
These are far from all the areas where DeFi solutions can be useful. However, they can be considered fundamental and those that will primarily be accessible to newcomers in this field. It's also worth considering that the decentralized finance market changes very rapidly, with new tools and offerings regularly appearing. For instance, we can note the growth in DeFi projects using passive portfolio management, as well as the actualization of DeFi insurance aimed at reducing risks when conducting financial operations with decentralized finance. More detailed information about all these categories can be found in the following sections.
Decentralized Applications
As mentioned above, most DeFi applications that allow using the decentralized finance system are deployed on the Ethereum blockchain. This platform provides developers with the ability to write smart contracts, which in turn allow quick deal-making of various types without intermediaries. Each individual financial operation incurs a commission, the level of which depends on system congestion.
Recently, DeFi applications have been actively created on blockchains like Binance Smart Chain (BSC). An example would be the DEX exchange PancakeSwap. Blockchains like Solana, Polkadot, and Avalanche are also being utilized. The exploration of new platforms is related to Ethereum becoming increasingly congested, which slows down its operation. Additionally, due to Ether's volatility, commissions are often quite high, which doesn't always suit users.
What is a Smart Contract and How is it Applied?
Smart contracts form the foundation for implementing financial operations within DeFi. Each is programmed for specific requirements. There's always a condition under which the contract becomes active, and the result of its execution is evaluated. For better understanding, let's consider a specific example:
- A user purchases a token that provides ownership of a certain security – for example, shares of a major company. According to the terms, the new owner will receive dividends at the beginning of each month. Accordingly, the smart contract specifies not only the token's cost but also indicates the dividend accrual date, their amount, and the duration of the payment period. This approach simplifies the described financial operations process, as they're all executed automatically without needing to involve a third party.
However, it should be considered that smart contracts have certain disadvantages. They represent code written by humans. This means contract execution conditions might be more favorable specifically to whoever proposes it. Moreover, the probability of errors in the contract structure cannot be excluded, which could lead to negative consequences for both parties. It's important to remember that even on blockchain, there's a threat of hacker attacks, so smart contract codes should be regularly reviewed and updated when necessary.
What are Decentralized Applications? What are Their Advantages and Disadvantages?
Smart contract launch and execution occur within blockchain-based decentralized applications. Externally, they might resemble standard cryptocurrency exchange applications or even have a more simplified interface. However, their operating principle is different. DeFi applications serve only as visualization of current smart contracts without providing any auxiliary functions. Centralized control is also absent here.
Several advantages characterize decentralized applications:
1. High reliability level. Smart contracts deployed on
blockchain cannot be forged – neither before their implementation nor
after deal conclusion. However, it's important to consider that smart
contracts will only be fully protected with regular technical audits
of their code.
2. Mass accessibility. Applications remain available and active
as long as the Ethereum platform exists.
3. Transparency. Anyone can audit smart contracts. All
information is publicly accessible.
However, transparency can also be considered a certain disadvantage. Since any user can access the code of any smart contract, they have a chance to find flaws and use them for subsequent hacker attacks.
Another feature of smart contracts is that after launch, they cannot be edited. On one hand, this protects DeFi from information forgery, but on the other hand, it excludes the possibility of making corrections to contract conditions. However, code error correction in terms of security remains available. Additionally, it should be mentioned that applications have certain limitations in their throughput capacity. This means that with increased activity, the speed of various operations may decrease.
What is Ether (ETH)?
Since DeFi is considered "within the framework" of the Ethereum blockchain in this case, it's worth remembering its main currency. We're talking about Ether or ETH. With its help, you can conduct various operations in decentralized applications. This currency can also be used to pay for goods and services in everyday life – there are now quite a few services providing the possibility of payment with such coins.
It's important to consider that if a user decides to choose a smart contract based on Ethereum, they'll need to use Ether to pay both for the purchase amount itself and the commission. If assets are stored in another coin, it must be converted using an exchange service or exchange.
What is Gas For?
As mentioned above, when conducting any financial operation on blockchain, a commission is charged. It's not fixed but directly depends on how congested the system is at a specific moment. However, it's the concept of gas that determines the commission amount. It's evaluated in units called gwei. The calculation is conducted at the rate of 1 gwei = 0.000000001 ETH.
- For example, a commission in an operation might be 200 gas units. One such unit, let's assume, equals 4 gwei. This means the total commission will be 800 gwei or 0.0000008 ETH.
However, it's important to consider that users can set gas prices themselves. If the system experiences high congestion, priority will be given to operations where this cost is maximum. Simply put, if a user wants to speed up their financial operations, they should set gas prices above average. Otherwise, they'll join a queue, and their requests will be processed after several others.
MetaMask Wallet in the Ethereum Ecosystem
If a user wants to start performing operations with decentralized finance, they'll definitely need to choose a wallet. For the Ethereum blockchain, MetaMask is provided as an option. It's available in different versions – as a web version, browser extension, or mobile application. Wallet functions will be identical in all these cases.
To become a MetaMask client, you'll need to follow a specific algorithm. It consists of the following stages:
Step 1: First, you need to download the wallet extension or application for Chrome, iOS, or Android. To do this, click the Download button located in the upper right corner of the main page of the site.
Step 2: Next, select the type of operating system of the device on which the user plans to use the wallet and click the download button.
Step 3: After the extension is downloaded, the system will offer to create a new wallet. The option to import data from a previously created wallet is also available. It's worth noting – to continue performing actions, the user will need to agree to MetaMask's terms. They're all written in sufficient detail, so you shouldn't ignore the opportunity to familiarize yourself with them.
Step 4: When creating a new wallet, you'll need to come up with a password.
Step 5: Next, the user will be offered the opportunity to additionally protect their wallet by using a secret phrase.
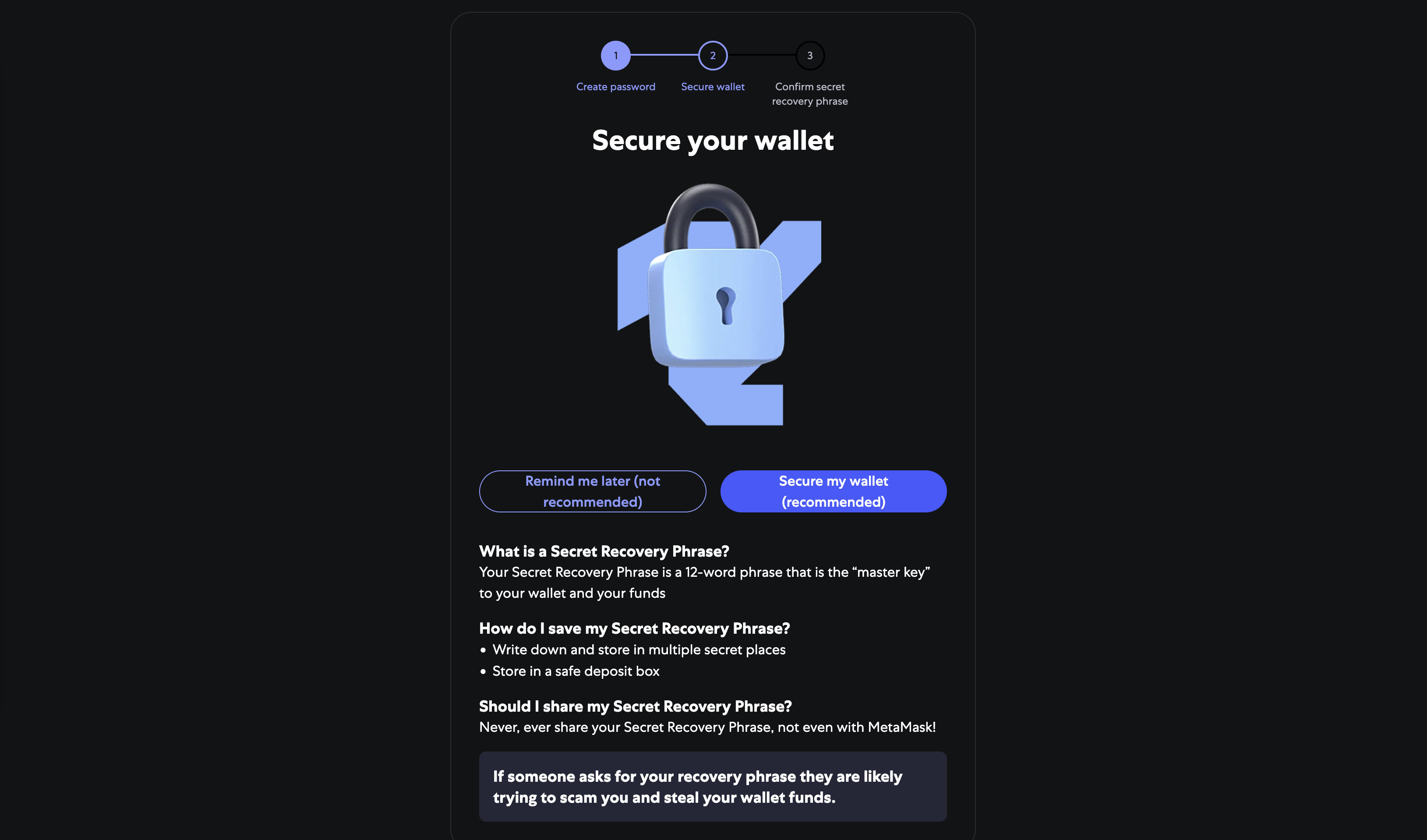
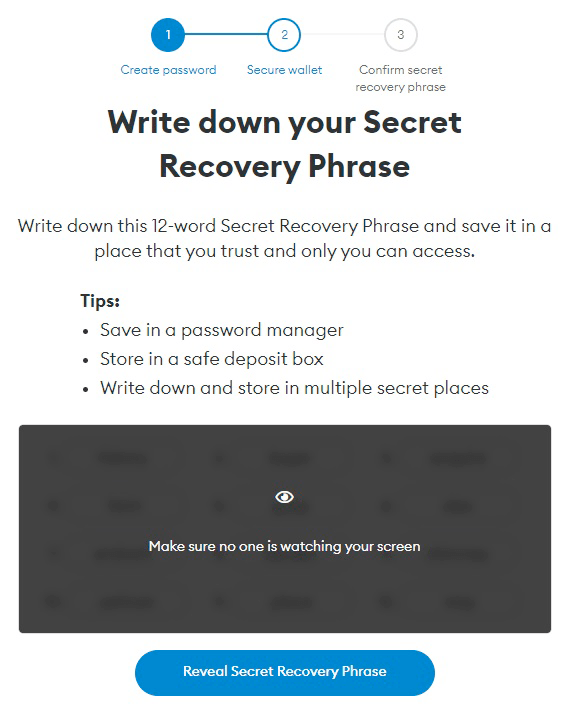
Step 6: Make sure no one nearby can see the screen. After this, confirm showing the secret phrase. This is exactly what will be needed to restore wallet access. It's worth noting that the secret phrase will need to be confirmed by entering three missing words.
Step 7: If all actions are performed correctly, the new MetaMask wallet will be created immediately.
The wallet itself will look as shown below.
To perform operations, for example, to top up this wallet's account, you need to use a key. It can be found on the main screen under the account name.
Decentralized Stablecoins: Advantages and Disadvantages of Use
All existing stablecoins can be divided into two categories. The first are centralized coins backed by national currency. For example, USDT can be attributed to this group. This currency is pegged to the dollar. That is, 1 USDT equals 1 USD. However, the reserves responsible for this stablecoin's existence are in closed access. Therefore, it's impossible to verify whether they're sufficient. This means that when purchasing any similar coins, a person might subsequently face risks.
Decentralized stablecoins backed by cryptocurrencies serve as an alternative. DAI can be considered an example. This coin is also pegged to the dollar, but its reserves are backed by Ether. Due to this coin's high volatility, DAI's backing is 1.5 to 1, while for centralized stablecoins this indicator equals 1 to 1. Additionally, users always have the opportunity to verify them. It's worth noting that DAI is the most widely used stablecoin in the DeFi ecosystem and shows very rapid growth in its circulation.
Decentralized Lending and Loans
Lending service is one of the most popular among users of financial systems – both banks and DeFi. However, in the first case, there are many barriers to obtaining loans and credits. Specifically, this involves the need to confirm identity, indicate income sources, minimum earnings, etc. Even with the possibility of using collateral, all the above factors can prevent obtaining credit.
Regarding decentralized finance, this situation doesn't occur. If a user possesses a sufficient amount of digital assets, they can use them as collateral. This will be sufficient for issuing credit or loans. That is, obtaining the needed amount will be much easier. As for lending conditions, they usually somewhat fall short of those established in centralized financial institutions.
It should also be considered that within DeFi, users are provided the opportunity to independently offer loans. Given that in such cases there's no third-party influence, there's no need to pay additional commissions and more. All this opens opportunities for those who want to take a suitable amount on credit without overpaying huge interest.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
We can confidently say that centralized exchanges currently have more weight in the cryptocurrency market than decentralized ones. However, the former have a certain disadvantage whose presence stimulates active DEX development. It's related to insufficient protection of user assets. During trading , clients place their funds on exchanges' internal accounts. If hacking is discovered, there's a high probability of losing absolutely all assets. And not every exchange will be ready to compensate such losses.
Regarding decentralized exchanges, the working system is completely different. All funds are stored by users in their wallets, which aren't tied to the exchange's internal accounts. DEX deals themselves are concluded through smart contracts: the user pays the required amount, and it immediately goes to the counterparty's account. No intermediaries are provided. Assets aren't transferred to the exchange's use. Considering all this, risks are significantly reduced – even in case of DEX hacking, fraudsters won't be able to access users' finances.
Liquidity Pools
It's important to consider that decentralized exchanges can operate on two principles. The first is the classic order book (similar to what's used in centralized exchanges), and the second is liquidity pools. With an order book, users can place orders , choosing market prices or indicating their own. However, often such orders have to wait quite a long time to be executed due to cryptocurrency high volatility. Liquidity pools can solve this problem. They play the role of certain reserves. Tokens accumulate in them, and when a trader wants to buy them, they don't need to wait for responsive offers. It's enough to choose a suitable token from the pool and immediately purchase it.
An additional advantage is that pools can be used not by just one specific exchange, but by several at once. This helps maintain or even increase liquidity. The cost of available tokens is also not stable. It depends on transaction volumes.
For an exchange to create such a pool, it needs to obtain a sufficient amount of coins. For this, users are provided the opportunity to make deposits and receive a certain percentage for this.
It's important to consider that such commissions can be unstable. Everything here depends on the activity of users wanting to use, for example, lending. If there are many such users, then considerable commission can be collected. Accordingly, the interest rate on deposits also increases. However, if activity is insufficient, depositors might receive only minimal interest.
Other Directions and Spheres of Decentralized Finance: Portfolio Management, Insurance
The decentralized finance sphere develops very quickly. Projects with new possibilities constantly appear, including decentralized portfolio management. In essence, it differs significantly from classic investment portfolio management, when asset management itself is transferred to a third party to minimize risks and increase profits. Here the goal is to exclude portfolio management functions as such. That is, certain tools are provided with which you can independently manage your own assets without involving a third party.
We're talking about a specially developed algorithm that can automatically perform trade selection. The user themselves won't have to deal with this. This significantly facilitates their participation – there's no need to analyze the market, forecast the liquidity of one coin or another, etc. An example would be the TokenSets platform, which has a built-in asset management strategy. This means the user won't have to monitor the market manually – the system will do everything for them.
Decentralized insurance should also be considered separately. It's of great importance because, despite high reliability levels, the decentralized ecosystem still involves several risks. They're related to the probability of smart contract code hacking. As mentioned above, decentralized finance in its full scope is available for audit. This is their undisputable advantage. However, it also leads to increased chances for fraudsters to calculate vulnerable elements for subsequent hacker attacks. This is why, if the amount of investment in smart contracts is large, it's important to think through ways to guarantee its preservation.
There are several smart contract insurance options:
- Nexus Mutual. This protocol allows insuring smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. It provides protection against code errors that could potentially lead to financial losses. It's important to consider that this doesn't include insurance against private key loss or in case of hacking – such incidents aren't covered by insurance. Insurance price depends on several factors, including insurance amount, period, etc. Each individual smart contract's characteristics are also evaluated.
- Opyn. This is an application allowing smart contract insurance. Protection is provided not only against technical errors but also against financial and administrative risks. Options – derivative financial instruments – are used for this. Simply put, they represent the right to buy or sell assets at a certain price within a specific timeframe.
Each user can independently decide whether to engage in smart contract insurance or do without it. However, it's important to understand that in DeFi there are no other options provided to protect assets. Although cases of technical failures, hacking, etc., are observed infrequently, it won't hurt to be safe.
Conclusion: Is DeFi the Future That Has Already Arrived?
In conclusion, it should be said that DeFi is a unique financial system that differs significantly from the traditional one. It's characterized by complete transparency and the absence of intermediaries and central bodies that manage assets – here the owner bears responsibility for all their finances. They receive all the ecosystem's advantages but must also regulate possible risks themselves.
Why are decentralized finances gaining such momentum? This has a simple explanation that lies in their accessibility and efficiency. Absolutely everyone can gain access to smart contracts. Location, social status, and other parameters don't matter. At the same time, there's no need to pay large commission amounts or other services. Additionally, there's always the possibility to choose the most profitable offers without any limitations or barriers. The centralized finance market hasn't yet been able to provide such conditions, which explains the growing competition. Whether DeFi is the future of the financial sector is still difficult to say. However, many prerequisites for this already exist.