Cryptocurrency Exchangers: History of Development, Operating Principles, and How to Choose
In this article, we will take a brief journey through the history of cryptocurrency exchangers, exploring how everything began using examples of the most famous platforms of that time. We will outline the main methods of acquiring and exchanging crypto and highlight the key operating principles of cryptocurrency exchangers from an ordinary user's perspective, noting their features and drawbacks. We will examine step-by-step instructions on how to use a crypto exchanger. In the concluding section, we will attempt to answer the question:
how do you choose the optimal service for convenient and secure cryptocurrency exchange in today's reality?
A Journey Through Cryptocurrency History
For many today, the existence of a global information network seems like a simple everyday phenomenon. It's hard to believe that back in the distant 1980s, the first steps were being taken to exchange brokerage data through information networks, and futuristic concepts of digital money were emerging. At that time, the entire idea revolved around the ability to execute trades for purchasing stocks and other financial assets very quickly.
If we recall the history of the first cryptocurrency's emergence, the purchase of Bitcoin for fiat currency occurred shortly after its appearance. This happened in 2009, when Martti Malmi sold 5,050 BTC to user NewLibertyStandard for $5.02. The money to cover the transaction was transferred to him via PayPal. The value of such an asset in USD or other currencies can now be easily calculated by checking monitoring services. Those same 5,050 BTC were used to launch a new service called New Liberty Standard. This is how the first Bitcoin exchanger appeared, which set Bitcoin's price at 1,309.03 bitcoins per $1.

Another well-known Bitcoin exchanger service is considered to be Bitcoin Market, which appeared in February 2010. There is little reliable information about the very beginning of their operations. A couple of years later, in 2012, members of the Bitcointalk forum tried to trace the history of the first exchanger operations, but concluded that information about the first trades and exchange rates of that period had not been preserved.
When recalling exchangers from those times, one cannot fail to mention the legendary Mt. Gox project, which for a long time was the world's largest Bitcoin exchanger until its bankruptcy in 2014. The project received its first impulse from programmer Jed McCaleb (the same developer of eDonkey 2000, and later the protocols for Ripple and Stellar). Then the baton was taken by Mark Karpelès, an original French geek living in Tokyo, known online by the nickname MagicalTux. And things took off from there.

As of August 2013, almost half of all transactions on the Bitcoin network were conducted through this platform. However, due to various reasons, including the loss of approximately 650,000 BTC, this platform went from being the world's largest to complete bankruptcy in just one year.
In the Russian-speaking environment, the BTC-E platform was well known. In spring 2014, by trading volume in the BTC/RUB pair, it ranked first (third in the BTC/USD pair). Three years later, servers and assets located in the United States were seized by the FBI, and the service itself was shut down.
At the same time, small exchanger services gradually appeared and began gaining popularity, through which one could quickly acquire cryptocurrency or conversely exchange it for national currency. They are called by different names: "digital currency service," "trading service," "electronic exchanger platform," "electronic currency exchanger point," or even "digital currency exchanger," but recently the terms "crypto exchanger" or "cryptocurrency exchanger" have become established.
Usually, a crypto exchanger is an online service through which all operations are performed electronically. As a rule, exchangers support operations via bank cards, money transfers, and other forms of payment in exchange for digital currencies. They most often operate outside the jurisdiction of Western countries while conducting operations including with their national currencies. At the same time, the ability to receive funds directly in cash is no longer a rarity. Naturally, in most cases, commissions are charged for such operations.
Main Methods of Acquiring and Exchanging Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency Wallets
It goes without saying that cryptocurrency must be stored somewhere, and cryptocurrency wallets are primarily created for this purpose. In addition, for their users, a convenient additional option for converting funds is typically offered using built-in third-party services. However, the exchange rate may be far from optimal, and commission sizes (for deposits, withdrawals, conversions) can be very substantial. Before depositing your funds into such a wallet, it's better to carefully study and, if possible, test with a small amount whether the actual situation matches your expectations.
Centralized Cryptocurrency Exchanges
In reality, crypto exchanges are not so much places for exchanging cryptocurrency as they are platforms for speculative earnings on exchange rates. There are quite a few of them: Binance, Huobi, KuCoin, and many others. Exchanges almost always have sufficiently large turnovers, so exchange commissions here are lower than in regular exchangers. At the same time, in 2022, KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) procedures are present on practically all exchanges. And where these don't exist, there's typically an increased risk of losing access to your funds at any moment. If going this route, it's better to choose large and proven platforms. Their main advantage is high liquidity, in other words, the ability to conduct exchanges almost instantly for fairly large amounts.
Online Exchangers
Perhaps the most popular way to simply buy or sell cryptocurrency reliably, quickly, and conveniently. Commission size, as a rule, does not exceed 1–3% and depends on the conditions of the specific platform (currency pair, transaction amount, payment method). However, there are unpleasant exceptions to the rules when commissions can turn out to be 5% or even 10%, so it's essential to pay attention to this before concluding a deal.
Among the disadvantages of this method, first and foremost, should be mentioned much lower liquidity than on centralized exchanges. There's a risk of losing on the spread between buying and selling prices, the probability of making errors when entering data, as well as difficulty in choosing a specific service from a large number of similar ones and the risk of encountering scammers during independent searches.
P2P Exchangers
Usually, everything is quite simple on P2P exchangers. A commission of about 1% of the transaction amount is typically paid by the seller (to the exchanger), while the buyer receives the exact amount according to the specified rate. The seller's funds are blocked during the exchange, and in case of their refusal to complete the deal, the buyer can file an appeal and still receive their funds.
However, in practice, not everything is always so smooth, and various fraud schemes exist that come down to either selling stolen coins or the possibility of not paying for the sent cryptocurrency. Despite rating systems and other user protection methods, such stories regularly occur on P2P exchangers.
Operating Principles of Electronic Currency Exchangers
There is a common opinion that technically all exchanger services are arranged identically and differ only in interface. In reality, this is not the case; these differences are simply hidden from users' eyes. The most important characteristics of an exchanger's operation remain:
- speed;
- anonymity;
- support.
Speed
All existing exchangers operate in one of three modes:
- automatic (fastest);
- semi-automatic;
- manual.
If the operating mode is not explicitly indicated on the website, this information can be clarified with the operator before making a transaction.
It should also be understood that exchange speed depends on the operation of payment systems and blockchains, especially regarding cryptocurrencies. In some cases, waiting may take several hours, but this is rather rare.
Anonymity (Verification Requirements)
Complete anonymity – no registration is provided, however, it's impossible to prove who the sender or recipient of coins is if such need arises.
Possibility of anonymity – registration is provided, but the user chooses whether to leave email or any other personal data.
Mandatory verification – necessity to confirm identity before conducting an exchange.
In practice, security and reliability sometimes conflict with anonymity, so it's worth making a thoughtful decision before exchanging. Verification is passed once, after which many exchange directions are transferred to automatic mode and are executed without any delays.
Support
Even having some experience using similar services, there's a probability of missing some detail or imagining the interface logic differently. More often, newcomers may find themselves in such situations, so the absence of online support is definitely a reason to look for another exchanger. Most websites provide the opportunity to communicate with a live operator, even without registration, since competent support service is exactly the helper that will certainly draw your attention to all essential details and will accompany you right up to the successful completion of the exchange.
There is a fairly simple way to check how good the support service is at an exchanger. For this, before starting work, it's sufficient to ask several general questions. Based on the promptness and content of responses, there will already be an approximate understanding of what feedback can be expected in the future.
How to Use a Cryptocurrency Exchanger
The exchange procedure at most exchangers is implemented according to the following algorithm:
Step 1. Go to the exchanger's website and open the exchange window (in most cases, this is the main page of the site).
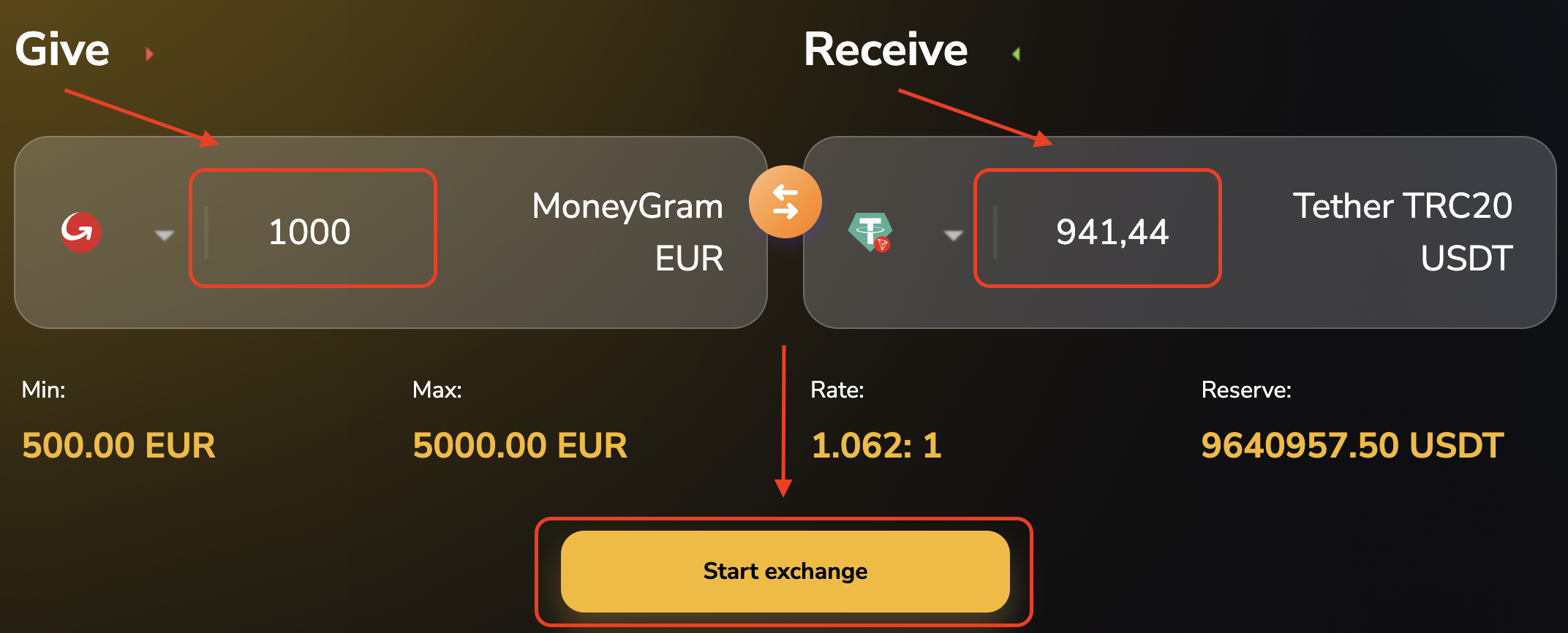
Step 2. Select the currency pair (what we give and what we receive) and enter the transaction amount.
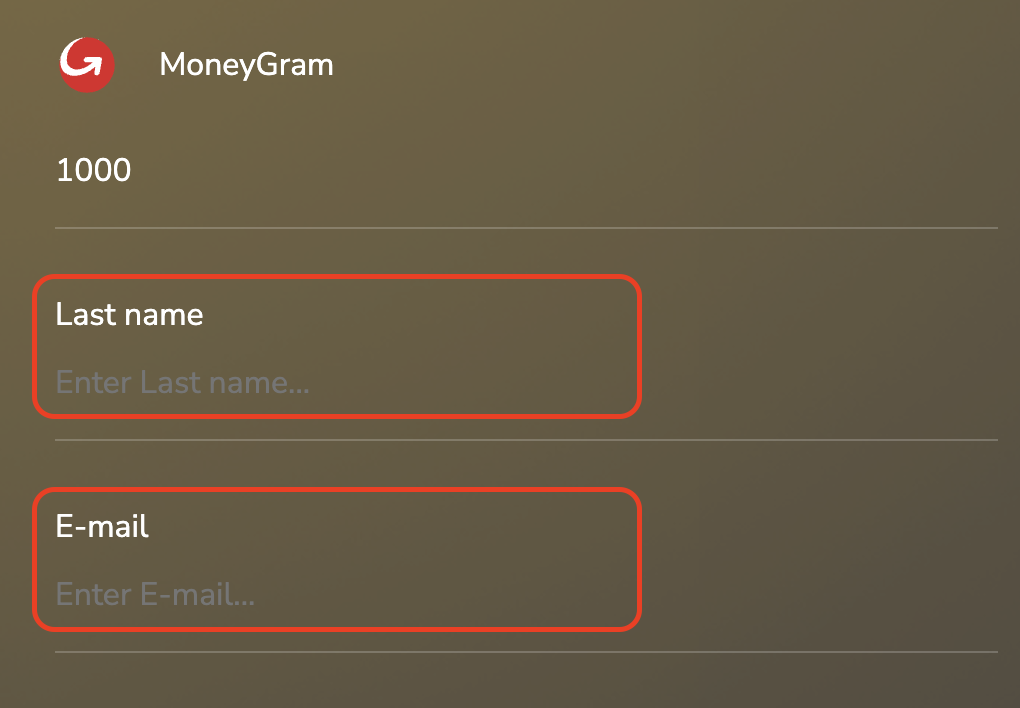
Step 3. Fill in the necessary contact information.
Step 4. Enter the wallet address for crediting cryptocurrency.
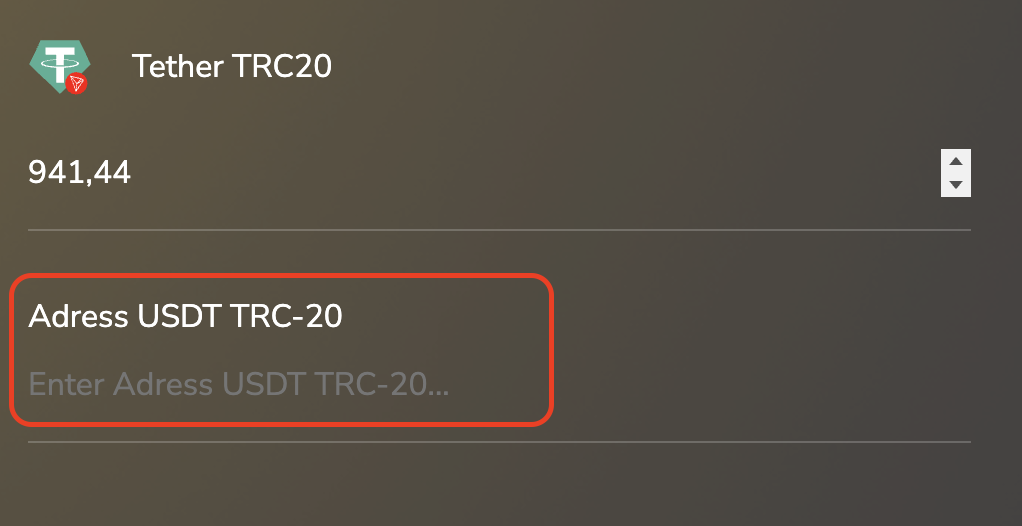
Step 5. Choose the payment method, check the transaction details, and transfer funds.
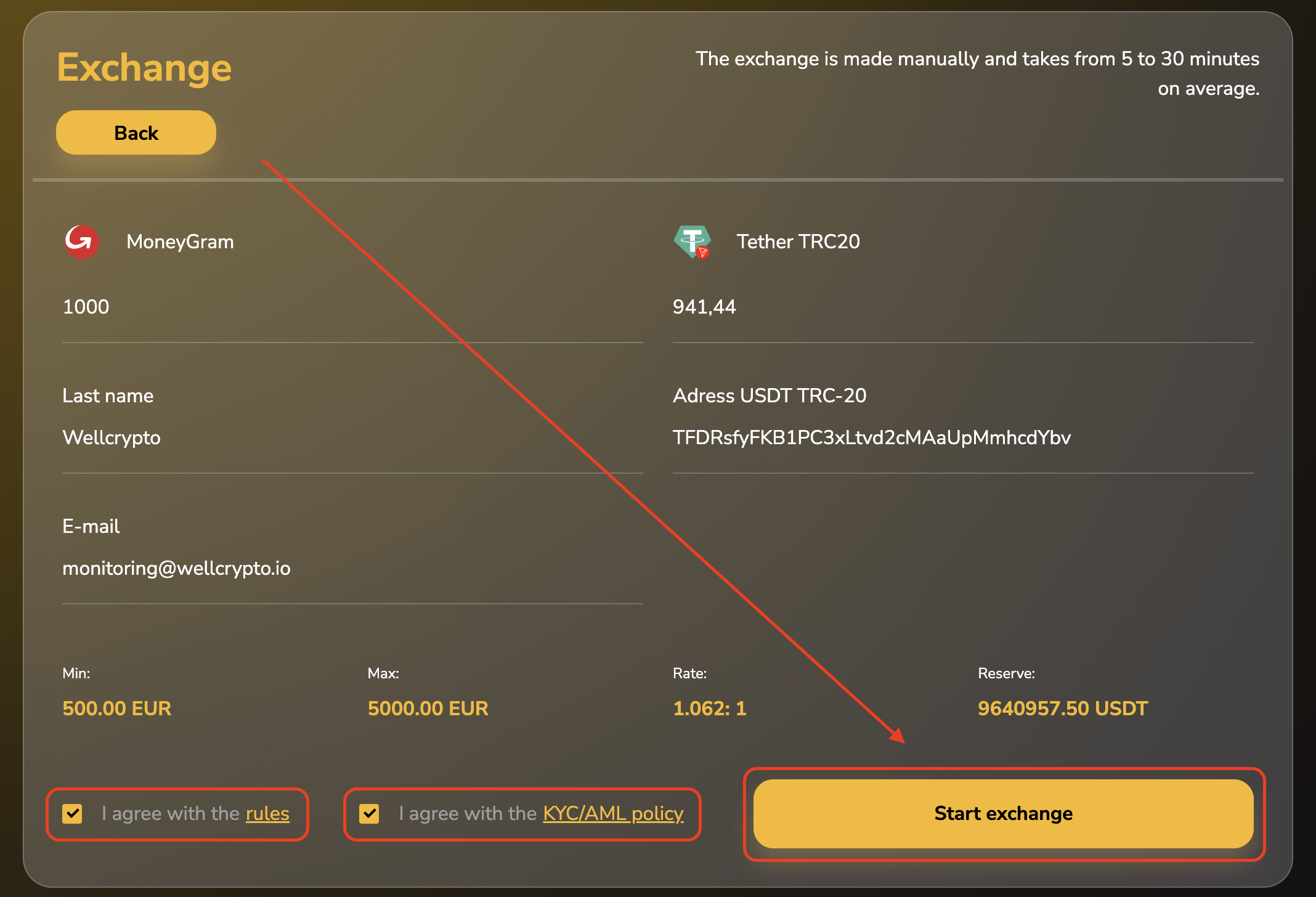
Step 6. Confirm the transaction execution.
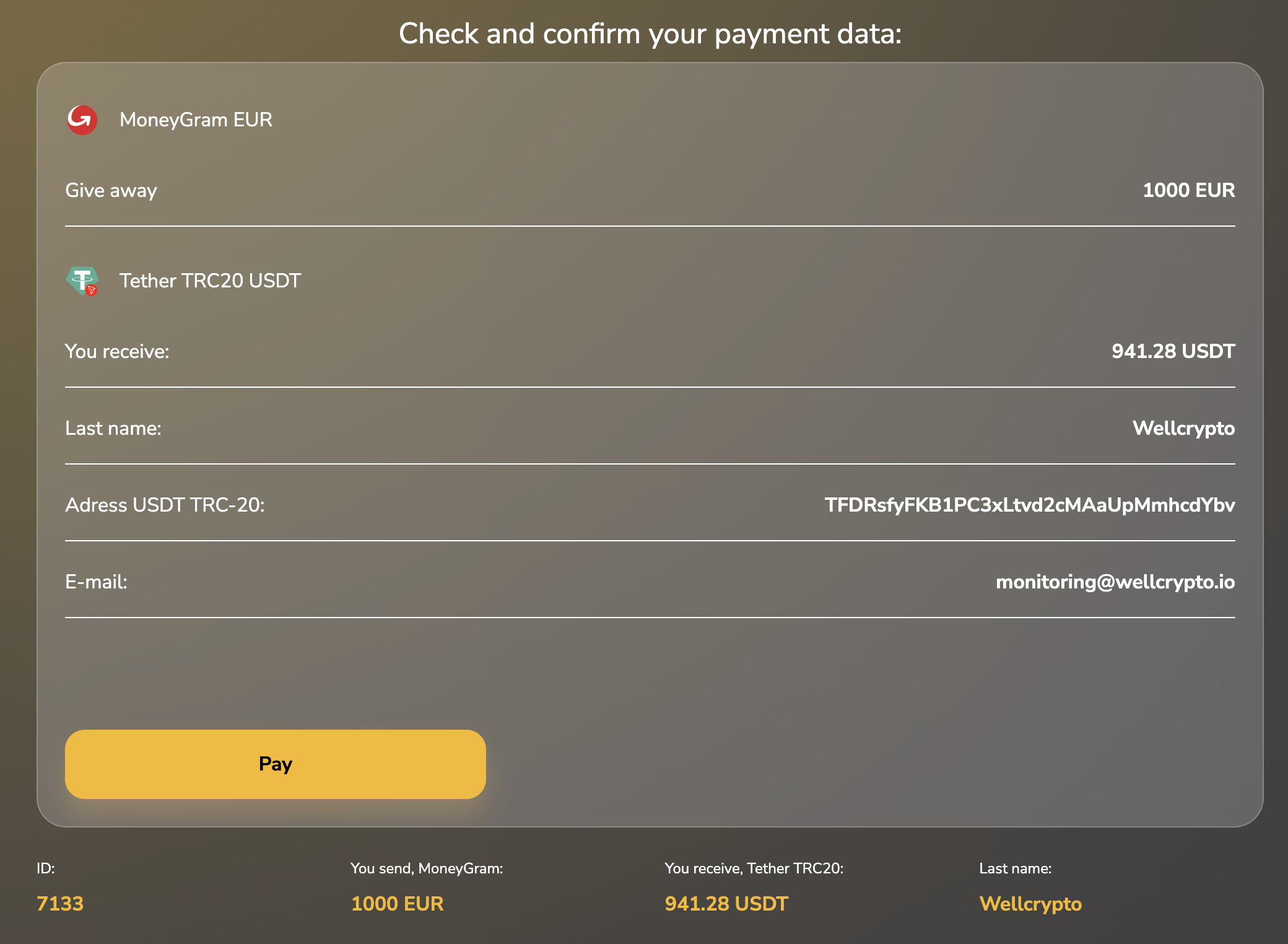
After these steps, all that remains is to wait for crediting, which is the final stage of the deal.
Besides the fact that this method of buying or exchanging cryptocurrency is very simple and easy, in implementation it has a fairly high level of security. At the same time, the possibility to exchange cryptocurrency without registration is preserved, ensuring freedom of choice in the matter of personal identification.
How to Choose a Cryptocurrency Exchanger
Everyone has the right to independently choose the optimal way to search for an exchanger service. You can spend a long time combing through search engines with queries, re-reading hundreds of forum pages and thousands of reviews, or conversely, open the first one you come across. In the end, the most important condition is stable operation and transaction security. You can maximize simplification of this process and simultaneously protect yourself from the risk of encountering scammers by using cryptocurrency exchanger monitoring services.
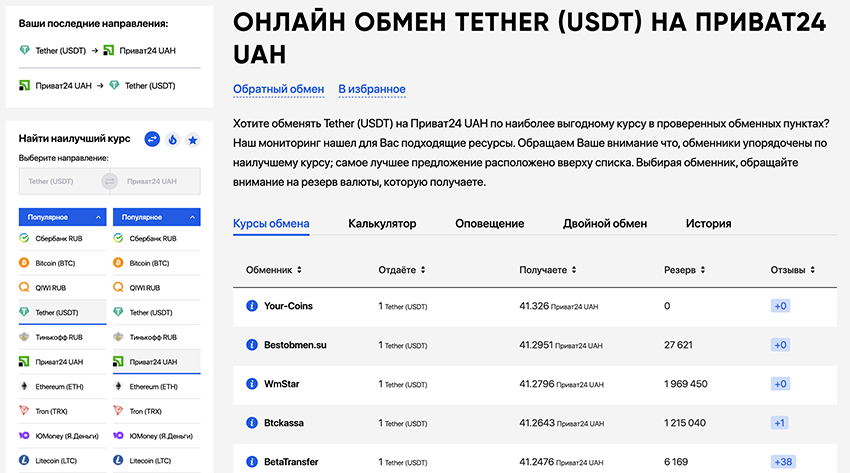
Choosing such a path, we get the opportunity to select the maximum number of suitable options according to specified criteria in just a few seconds. Among such criteria, you can specify the most favorable rate, choose a specific amount you want to give or receive as a result of the exchange, select available reserves, etc. But most importantly, this significantly reduces the risk of encountering fraudsters or incompetent specialists who, intentionally or due to ignorance of some details, will lead to unnecessary expenses or complete loss of funds.
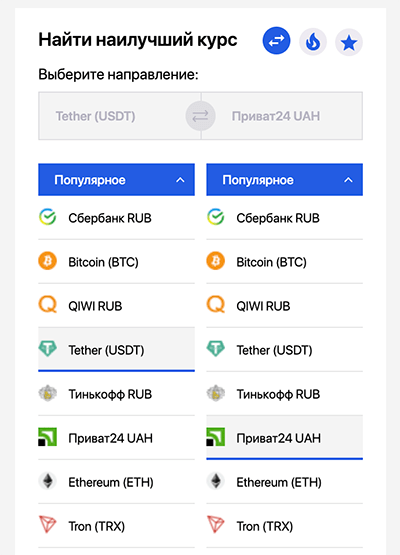
On the main page of the monitoring service, there's always a menu that can be used to specify the desired exchange direction and immediately get a complete list of exchangers that support this direction at the moment. Then you can familiarize yourself with a brief description, operating mode, reviews, and after that make a decision about which service to prefer.
Many years of experience working with exchangers allows us to highlight a fairly extensive list of criteria that should be paid attention to when choosing. Here are the most important signs when selecting a reliable exchanger service:
- operator response speed and quality of support service work;
- suitable working hours (not all work 24/7);
- conditions (verification) and commissions for a specific transaction;
- service interface (everyone decides for themselves what is convenient);
- available payment systems and tools;
- reserve amounts;
- exchanger age (time of presence in the market);
- user reviews (their quantity, ratio of positive and negative reviews).
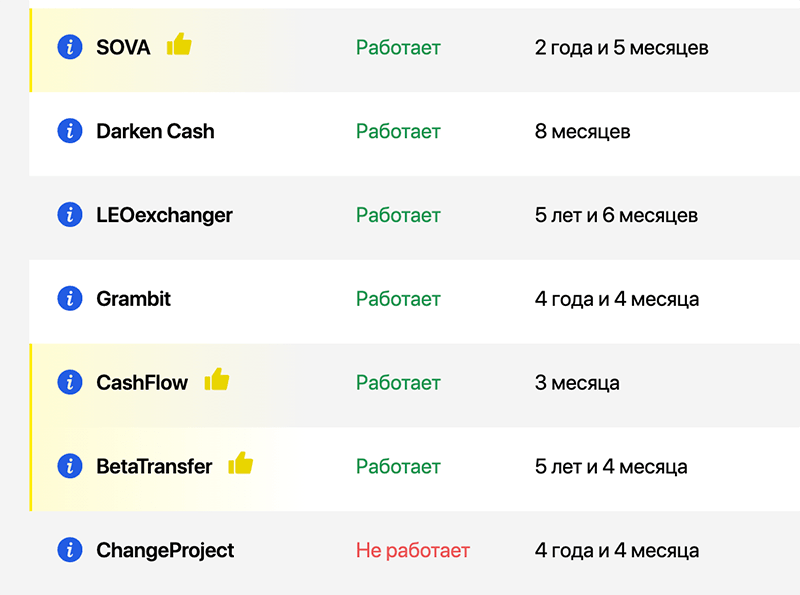
After studying data from exchanger monitoring services, it won't be superfluous to pay attention to the reputation of the chosen service and transaction security. If anything seems suspicious or simply strange to you, it would be reasonable to start the first interaction with the service with a small amount. Having made sure that everything works properly, you can increase exchange amounts.
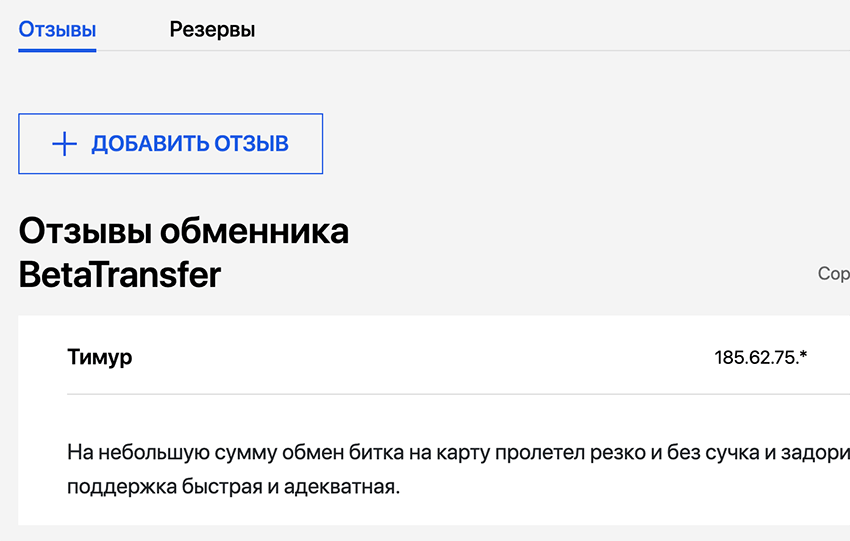
Cryptocurrency exchanger services often ask to register and undergo verification. If you register, you can always see the application status and history of your exchanges in your personal account. In practice, this is more reliable and convenient. Regarding verification, there are diametrically opposite opinions, but it should be understood that security and reliability sometimes conflict with anonymity. It would be more prudent to think about and make a decision on this matter before starting the exchange. In exchanger services, the verification procedure needs to be completed only once, after which many exchange directions can be transferred to automatic mode and will be executed without delays.
Thus, in current realities, cryptocurrency exchangers remain a fairly convenient tool if you face the task of quickly exchanging crypto for familiar fiat money. And if you use the selection criteria proposed above, choosing a suitable service for cryptocurrency exchange among the multitude of websites will not be so difficult.